|
||
|
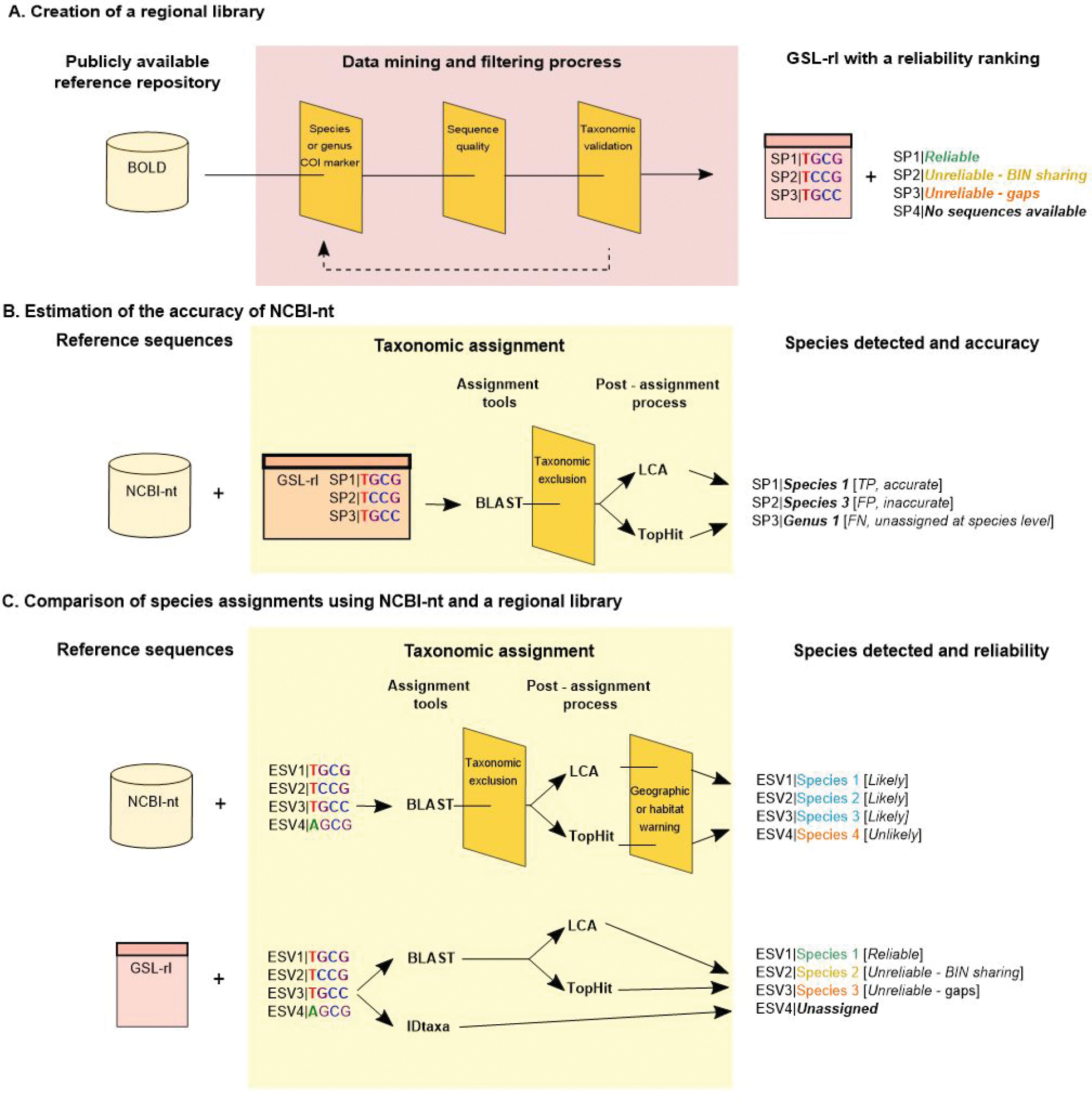
Schematic representation of the three main steps of this study. A Creation of a regional library for metazoans from the Gulf of St. Lawrence (GSL-rl). Sequences were selected from BOLD and curated through multiple filtering and auditing steps (see Fig. S1 for more details on filtering and auditing parameters). Species or genus were added through an iterative process to further improve the regional library. Each species in the GSL-rl was ranked based on sequence availability and sequence similarity to closely related species in the Gulf of St. Lawrence; B Estimation of the accuracy and precision of NCBI nucleotide database (NCBI-nt) using the reference sequences from the regional library. Taxonomic assignments were performed using NCBI-nt over the reference sequences from GSL-rl, using the Blast+ tool blastn (hereafter BLAST; Camacho et al. 2009). Assignment results were filtered based on taxonomic identity, then a least common ancestor (LCA) or a TopHit method were used to assign a unique taxon identity to each sequence. Each assignment was then classified as a true positive (TP, accurate), a false positive (FP, inaccurate) or a false negative (FN, unassigned at the species level). Performance parameters were derived from this classification; C Comparison of species assignments and their reliability using NCBI-nt or GSL-rl. Taxonomic assignments of ESVs from a metabarcoding dataset were performed with BLAST and with the classifier IDtaxa (Murali et al. 2018). For NCBI-nt, the species ranking involved a plausibility filter based on the location. For GSL-rl, the species ranking was directly provided with the library (see methods for more details). |