|
||
|
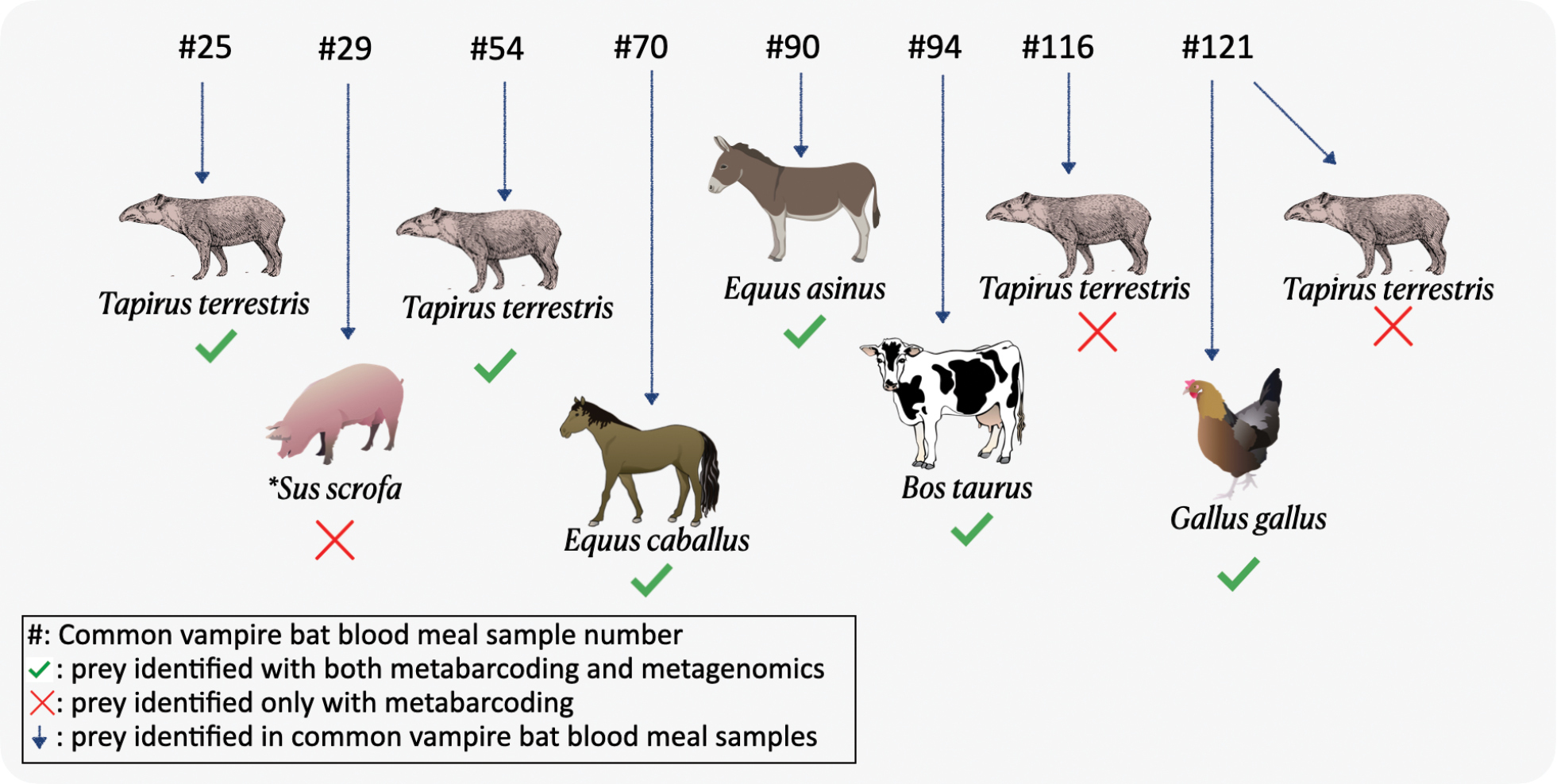
Prey identification of common vampire bat blood meal samples using shotgun metagenomics as compared to metabarcoding (Bohmann et al. 2018). Green ticked symbols signify consensus between both high-throughput sequencing (HTS) approaches. Red crossed symbols signify prey taxa identified using metabarcoding but not identified using metagenomics. *Sus scrofa was identified in sample 29 only after additional analyses were carried out with access to dietary information as determined from a previous metabarcoding study of the same common vampire bat blood meal samples (Bohmann et al. 2018). Some of the elements included in the figures were obtained and modified from the Integration and Application Network, University of Maryland – Center for Environmental Science (https://ian.umces.edu/symbols/), and BioRender.com. Image of tapir from Foresman (2007). |